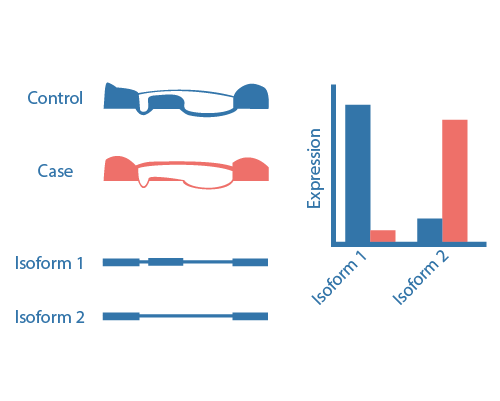
Alternative splicing events are pervasive in eukaryotes generating distint mRNAs by a differentially selection mechanisms within the pre-messager RNA. Alternative splicing mechanisms can include cassete exon, alternative 5' splice site, alternative 3' splice site, mutually exclusive exons, exon scrambling, intron retention, alternative promoter and alternative polyadenylation events. Methodologies for detection and analysis of these alternative splicing events fall into three major categories: isoform-based, exon-based, and event-based methods. Isoform based methods first assembly the full-length transcripts and then estimate their relative abundances. Exon-based methods detect alternative splicing by comparing the distribution of reads on exon and junctions between comparisons. This methods only detects the differentially expressed exons/junctions and not the type of event. In event-based methods, splicing events themselves are quantified using the fraction of mRNAs that contains a specific form of that event. Exon-based methods have a greater accuracy to detect splicing events and are appropriate if the focus is on the event themself and not the study of the whole isoform.
The first step in any RNA-Seq workflow is to assess the quality of the sequenced reads. A first quality control (QC) step is recommended for the assessement of contaminations, bias and errors in raw sequences. By addressing these issues we can reduce the impact of these errors in downstream analysis.
In this step, reads are aligned to either the species reference genome or transcriptome using a splicing-aware aligner sofware.
After the alignment step, reads are assigned to a gene or a transcrip which is then used to estimate expression levels of that gene/transcript.
In the last step, an additional quality control step assessing the percentage of reads mapped to the transcriptome versus unmapped will be conducted. This step can when detect contaminations on the extraction or library construction steps which can impair the correct analysis of the data.