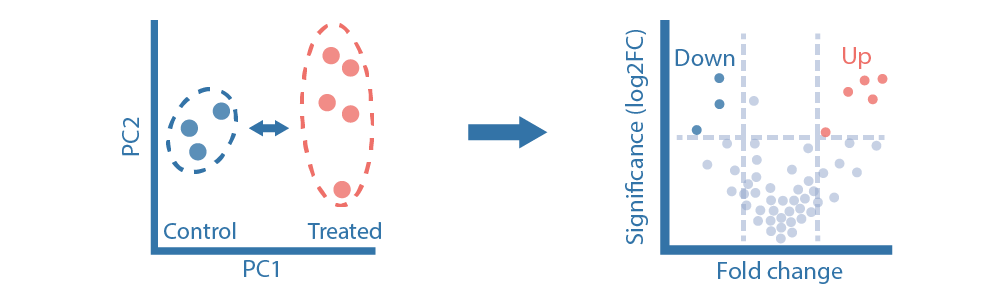
RNA-seq is a powerfull technique for measuring gene expression and transcription activation at genome-wide level, allowing to assess changes in cell biology associated with a phenotypic observation (e.g. disease). Transcriptome analysis captures information on splicing events and post-transcriptional modiffication which occur during mRNA processing, not detected by DNA sequencing. Additionally, the primary output of RNA-seq, counts of reads, have a high degree of agreement with qRT-PCR, both at absolute and relative gene expression levels. Two transcriptome sequencing modalaties are available to researchers, polyadenylated (poly-A) mRNA (mRNA-seq) and whole transcriptome sequencing. Whole transcriptome sequencing gives the the most comprehensive view possible by sequencing all coding and non-coding RNA transcripts (lncRNA, circRNA and sRNA). This strategy requires depletion of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) before library construction, since they can make up between ~80 to 98% of all RNA molecules in a sample. Additionaly, for sequencing of sRNA, special technical considerations should be undertaken before sequencing. For eukaryotes, mRNA-seq provides a more cost-efficient solutions for RNA sequencing by enriching for RNAs with poly(A) tails, such as message RNAs (mRNAs). The benefit of this approach is that it targets the full length, mature protein coding poly-A transcripts alone.
The first step in any RNA-Seq workflow is to assess the quality of the sequenced reads. A first quality control (QC) step is recommended for the assessement of contaminations, bias and errors in raw sequences. By addressing these issues we can reduce the impact of these errors in downstream analysis.
In this step, reads are aligned to either the species reference genome or transcriptome using a splicing-aware aligner sofware.
After the alignment step, reads are assigned to a gene or a transcrip which is then used to estimate expression levels of that gene/transcript.
In the last step, an additional quality control step assessing the percentage of reads mapped to the transcriptome versus unmapped will be conducted. This step can when detect contaminations on the extraction of library contruction steps which can impair the correct analysis of the data.